It looks a lot like a return to the past. Founded in 1949 to defend against the “Soviet threat,” the NATO alliance is facing a return to mechanized warfare, a huge increase in defense spending, and potentially a new Iron Curtain falling across Europe. After struggling to find a new post-Cold War role, countering terrorism following the September 11 attacks on the United States in 2001 and a humiliating withdrawal from Afghanistan in 2021, NATO is back encroaching on its original nemesis.1
U.S. Plans for the Establishment of Global Hegemony: 1945-47
During World War II an “unnatural alliance” was created between the United States, Great Britain, and the former Soviet Union. What brought the three countries together—the emerging imperial giant (the United States), the declining capitalist power (Great Britain), and the first socialist state (the Soviet Union)—was the shared need to defeat fascism in Europe. Rhetorically, the high point of collaboration was reflected in the agreements made at the Yalta Conference, in February 1945, three months before the German armies were defeated.

At Yalta, the great powers made decisions to facilitate democratization of former Nazi regimes in Eastern Europe, a “temporary” division of Germany for occupation purposes, and a schedule of future Soviet participation in the ongoing war against Japan. Leaders of the three states returned to their respective countries celebrating the “spirit of Yalta,” what would be a post-war world order in which they would work through the new United Nations system to modulate conflict in the world.
Big Three leaders pose for photo outside historic Yalta conference. [Photo: history.com]Within two years, after conflicts over Iran with the Soviet Union, the Greek Civil War, the replacement of wartime President Franklin Roosevelt with Harry Truman, and growing challenges to corporate rule in the United States by militant labor, Truman declared in March 1947 that the United States and its allies were going to be engaged in a long-term struggle against the forces of “International Communism.” The post-war vision of cooperation was reframed as a struggle of the “free world” against “tyranny.” It was really a struggle between two kinds of political/economic orders: one socialist, another capitalist.
The Economic Foundations of a New World Order
In addition to Truman’s ideological crusade, his administration launched an economic program to rebuild parts of Europe, particularly what would become West Germany, as capitalist bastions against the ongoing popularity of Communist parties throughout the region. Along with the significant program of reconstructing capitalism in Europe and linking it by trade, investment, finance and debt to the United States, the U.S. with its new allies constructed a military alliance that would be ready to fight the Cold War against International Communism.
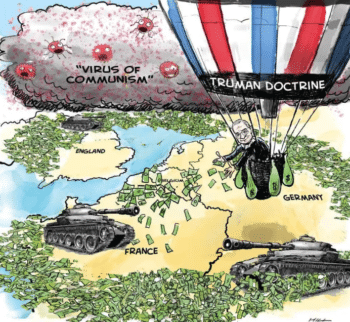
For Joyce and Gabriel Kolko (The Limits of Power, 1972) and other revisionists, the expansion of socialism constituted a global threat to capital accumulation. With the end of the Second World War, there were widespread fears that the decline in wartime demand for U.S. products would bring economic stagnation and a return to the depression of the 1930s.
The Marshall Plan, lauded as a humanitarian program for the rebuilding of war-torn Europe, was at its base a program to increase demand and secure markets for U.S. products. With the specter of an international communist threat, military spending, another source of demand, would likewise help retain customers, including the U.S. government itself. The idea of empire, which William Appleman Williams so stressed (The Tragedy of American Diplomacy, 1959), was underscored by the materiality of capitalist dynamics.
The Marshall Plan inspired European integration of states that were major recipients of Marshall Plan funds. The first significant economic organization, The European Coal and Steel Community, became operational in 1952. Its membership included France, West Germany, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. It encouraged the production and trade of core resources such as coal, steel and iron. In 1957, the purview of the ECSC was expanded with the creation of the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom).

Other, overlapping European institutions were created during the 1950s and beyond involving the original six and additional countries. In May 1960 seven European nations, not in the EEC, formed the European Free Trade Association to foster trade and economic integration. (In 1973, three countries including Great Britain joined the EEC).
Finally in 1992, after the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Maastricht Treaty established the European Union (EU) which, by 2019, had 27 member countries (nine from the former Soviet bloc) with a GDP of 16.4 trillion euros (the EU currency), constituting 15% of world trade. In addition, European nations are embedded in a network of regional and international organizations that deal with trade, finance, indebtedness, security and human rights. (See the diagram below.)
The reigning scholarly study of these efforts in the 1960s and beyond, integration theory, postulated that the greater the cross-national interactions of European countries the lesser the likelihood of war among them. Studies were carried out designed to discover how and why integration seemed to be working in Europe but less so in troubled locations, such as on the African continent.
But from another vantage point “regional integration” inspired by and connected to the United States political economy can be seen as a near complete fruition of the vision of U.S. and capitalist hegemony initiated in those crucial early years after World War ll. The 21st century policy program of the United States and most of Europe has been to establish on a global basis a capitalist economic model.

Ideologically, the presupposition is that this model is historically exceptional and therefore must resist threats to its survival and growth. The so-called communist threat of the 1940s is the “authoritarian” threat of the current century. And to the extent that capitalist hegemony is not achievable by consent, it might need to be instituted by force.
While world history is more complicated than this narrative suggests, there is enough plausibility to it to justify fears, particularly when the military instrument—NATO—expanded eastward. From this point of view, NATO itself may not be the only threat to countries in Europe and Asia. But the use of it as a part of global expansion of economic and political institutions, coupled with the ideological expression of American exceptionalism, could create fear and aggression.
NATO As the Military Arm of a Drive for a Hegemonic Global Political Economy
Representatives of Western European countries met in Brussels in 1948 to establish a program of common defense and one year later with the addition of the United States and Canada, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was formed. The new NATO charter, inspired largely by a prior Western Hemisphere alliance, the Rio Pact (1947), proclaimed that “an armed attack against one or more of them…shall be considered an attack against them all” which would lead to an appropriate response.

[Source: twitter.com]The Charter called for cooperation and military preparedness among the 12 signatories. After the Soviet Union detonated its first atomic bomb and the Korean War started, NATO pushed ahead with the development of a common military command structure with General Eisenhower as the first “Supreme Allied Commander.”
After the founding of NATO and its establishment as a military arm of the West, the Truman administration adopted the policy recommendations in National Security Council Document 68 (NSC 68) in 1950 which declared that military spending for the indefinite future would be the number one priority of every presidential administration.
As Western European economies reconstructed, Marshall Plan aid programs were shut down and military assistance to Europe was launched. Greece and Turkey joined NATO in 1952 and, fueling the flames of the Cold War, West Germany was admitted to NATO in 1955. (This stimulated the Soviet Union to construct its own alliance system, the Warsaw Pact, with countries from Eastern Europe.)
Image from first NATO summit. [Source: nato.int]During the Cold War, NATO continued as the only unified Western military command structure against the “Soviet threat.” While forces and funds only represented a portion of the U.S. global military presence, the alliance constituted a “trip wire” signifying to the Soviets that any attack on targets in Western Europe would set off World War III. Thus, NATO provided the deterrent threat of “massive retaliation” in the face of a first-strike attack.
With the collapse of the former Warsaw Pact regimes between 1989 and 1991, the tearing down of the symbolic Berlin Wall in 1989 and, finally, the collapse of the Soviet Union itself in 1991, the outspoken purpose for maintaining a NATO alliance presumably had passed. However, this was not to be.
In the next 20 years after the Soviet collapse, membership in the alliance doubled. New members included most of the former Warsaw Pact countries. The functions and activities of NATO were redefined. NATO programs included air surveillance during the crises accompanying the Gulf War and the disintegration of the former Yugoslavia.

[Source: youtube.com]In 1995, NATO sent 60,000 troops to Bosnia and in 1999 it carried out brutal bombing campaigns in Serbia with 38,000 sorties. NATO forces became part of the U.S.-led military coalition that launched the war on Afghanistan in 2001. In 2011 a massive NATO air war on Libya played a critical role in the overthrow of the Gaddafi regime.
An official history of NATO described the changes in its mission: “In 1991 as in 1949, NATO was to be the foundation stone for a larger, pan-European security architecture.” The post-Cold War mission of NATO combines “military might, diplomacy, and post-conflict stabilization.”

The NATO history boldly concludes that the alliance was founded on defense in the 1950s and détente with the Soviet Union in the 1960s. With the collapse of Communism in the 1990s, it became a “tool for the stabilization of Eastern Europe and Central Asia through incorporation of new Partners and Allies.” The 21st century vision of NATO has expanded further: “extending peace through the strategic projection of security.” This new mission, the history said, was forced upon NATO because of the failure of nation-states and extremism.
NATO and Ukraine Today
Conference in Belgrade, Yugoslavia, March 2019, exposes NATO’s bombing of Yugoslav children. Reviewing this brief history of NATO, observers can reasonably draw different conclusions about NATO’s role in the world than from those who celebrate its world role. First, NATO’s mission to defend Europe from aggression against “International Communism” was completed with the “fall of Communism.” Second, the alliance was regional, that is pertaining to Europe and North America, and now it is global. Third, NATO was about security and defense. Now it is about global transformation.

Fourth, with the U.S. as NATO’s biggest supporter in terms of troops, supplies and budget (22-25%), NATO is an instrument of United States foreign policy. Fifth, as a creation of Europe and North America, it has become an enforcer of the interests of member countries against, what Vijay Prashad calls, the “darker nations” of Asia, Africa and the Middle East. Sixth, NATO has become the 21st century military instrumentality of global imperialism. And, finally, there is growing evidence that larger and larger portions of the world’s people have begun to stand up against NATO.
In the context of this complex history, Russia launched its invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, following eight years of war in Eastern Ukraine. After four weeks thousands of Ukrainians have been killed and more than four million have fled their cities and towns. The President of Ukraine, spokespersons from some NATO countries, and some U.S. politicians have called for a “no-fly zone” over Ukraine which would escalate the war to a near-nuclear war situation. In addition, NATO countries, and particularly the United States, have dramatically increased military expenditures. Impactful economic sanctions have been leveled against Russia, and economic instabilities are beginning to affect Europe and the United States. In addition, vital work around combating climate change has been stalled and important pieces of legislation to fulfil social needs have been eliminated from legislative consideration.
What Needs to Be Done?
To quote a tired but true slogan, “war is not the answer.” The Russian invasion of Ukraine threatens the lives and property of Ukrainians, the lives of Russian soldiers and protesters, raises fears of an escalation of war throughout Europe, and raises the danger of nuclear war.

“We” need to support “back-channel negotiations” in process as occurred during the Cuban missile crisis, demands that Russia stop the violence and withdraw its military forces from Ukraine, diplomacy at the United Nations, and summit meetings of diplomats from Russia, Ukraine and Europe. And conversations on the agenda should include forbidding Ukraine from joining NATO, establishing regional autonomy for Ukraine citizens who want it, pulling back NATO bases from Eastern European states, and/or abolishing NATO itself because the reason for its creation in the first place, defending against the Soviet Union, no longer exists.
The “we” at this moment could be a resurgent international peace movement, taking inspiration from peace activists in Russia and around the world. As horrible as this moment is, it is potentially a “teachable moment,” a moment when peace becomes part of the global progressive agenda again and people all around the world can begin to examine existing international institutions such as NATO.
And while we react with shock and condemnation of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, whatever the complicated and understandable motivations, we need to be familiar with the historic context of the very dangerous warfare that we are living through now.
As James Goldgeier wrote more than 20 years ago on a Brookings Institution web page:
The dean of America’s Russia experts, George F. Kennan, had called the expansion of NATO into Central Europe ‘the most fateful error of American policy in the entire post-Cold War era.’ Kennan, the architect of America’s post-World War II strategy of containment of the Soviet Union, believed, as did most other Russia experts in the United States, that expanding NATO would damage beyond repair U.S. efforts to transform Russia from enemy to partner.”
